Dental Regeneration

Dental treatments are a matter of trust:
Our experience and expertise are something you can rely on.
Biomaterials from Geistlich Pharma AG are the most frequently used materials in regenerative dentistry worldwide. Over 100 million patients have been treated with them.
- Geistlich products are high-quality Swiss biomaterials.
- They have been evaluated in more than 1,000 studies globally.
- The meticulous selection of raw materials, combined with a strictly controlled manufacturing process, ensures Geistlich biomaterials meet high safety and tolerability standards.
Their safety has been assessed by international and national regulatory bodies.
GEISTLICH PATIENT VIDEOS
Tooth Out – What’s Next?
What happens after tooth removal?
Following a tooth extraction, bone and soft tissue tend to shrink if no restorative treatments are planned. Besides poor aesthetic results, inadequate bone volume can require a secondary procedure for implant stability or cause a gap under a bridge.
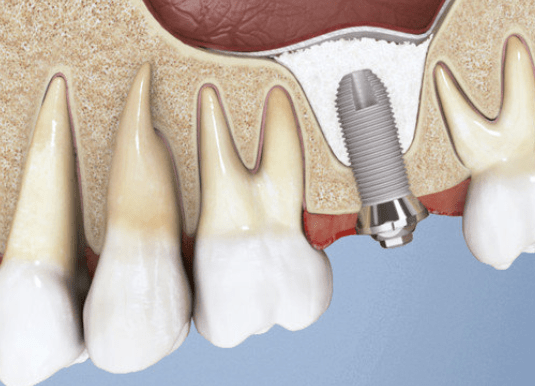
Filling the extraction socket with a bone substitute immediately after tooth extraction helps preserve bone volume, supporting better treatment outcomes. If an implant is placed soon after extraction, bone substitutes around the implant also stabilize bone volume.
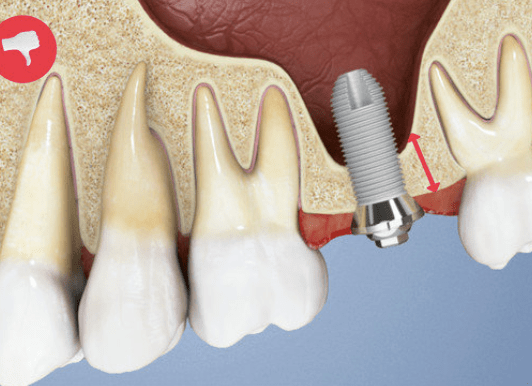
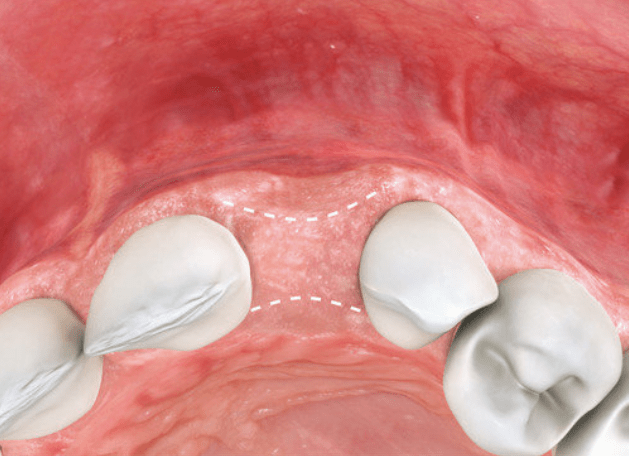
Without preventive measures…
The socket collapses over time due to natural bone resorption. This results in poor aesthetics with implant restorations and unattractive gaps between bridges and gums.
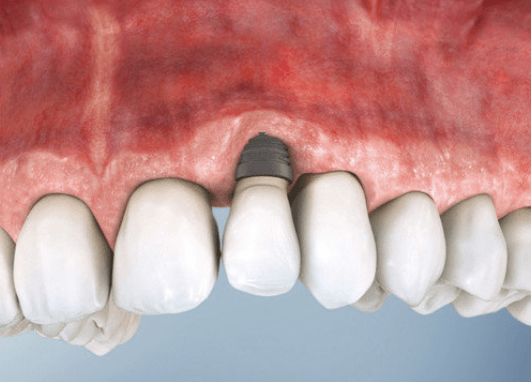
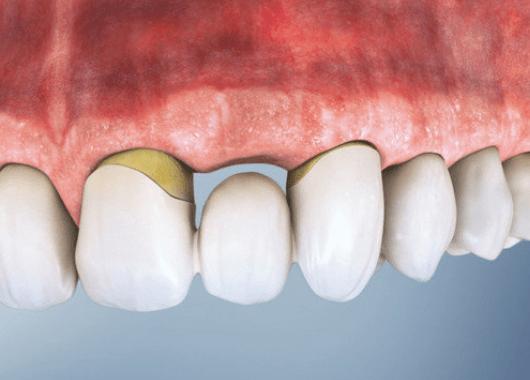
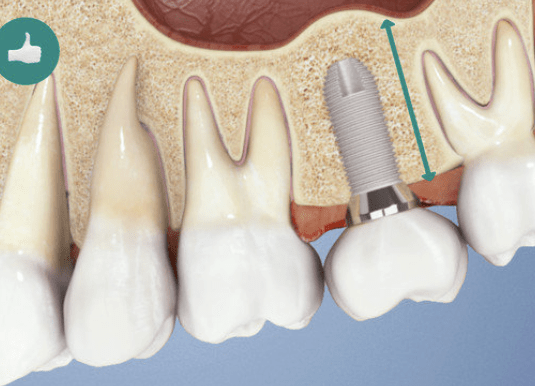
With preventive measures…
Ridge preservation — filling the empty socket with a bone substitute — helps retain bone volume and shape. Geistlich Biomaterials provide flexibility in choosing the final restoration (implants or bridges).
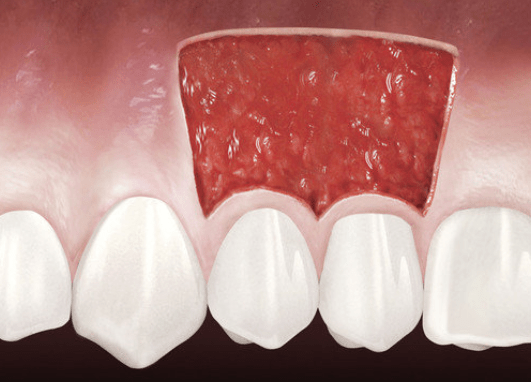
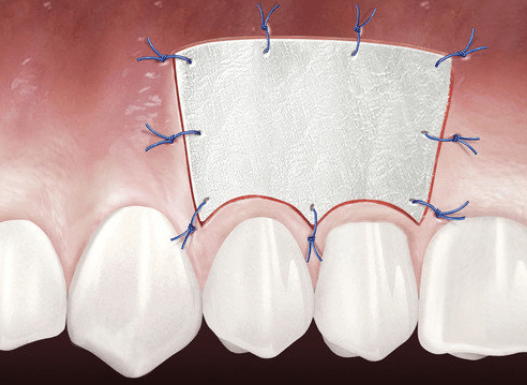
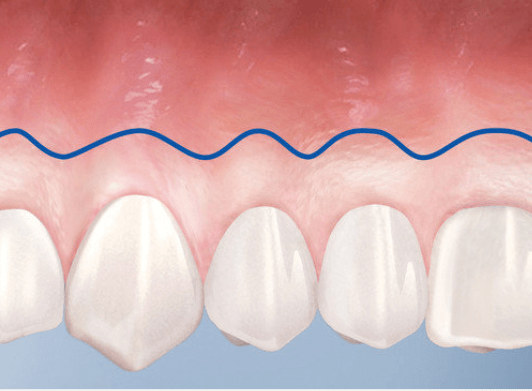
Inflamed Gum – Now What?
What happens when gum tissue is unhealthy?
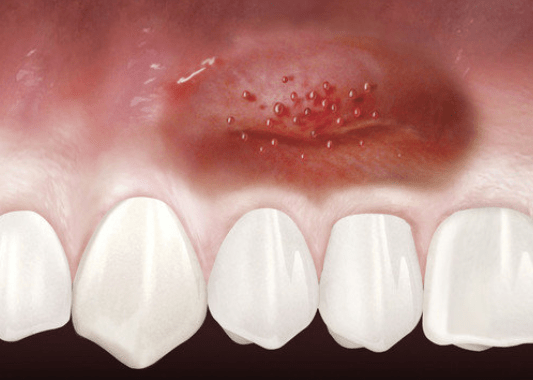
Gum tissue surrounds the teeth like a tight cuff. Insufficient healthy gum can lead to inflammation, pain, bleeding, and bone or gum loss.
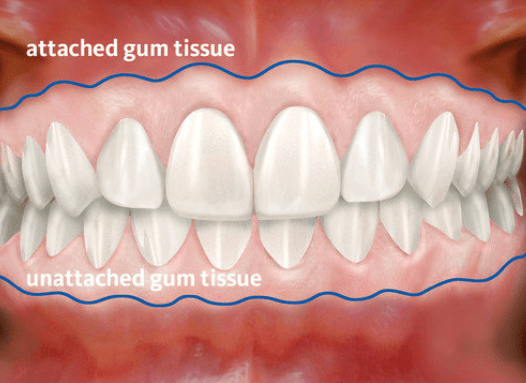
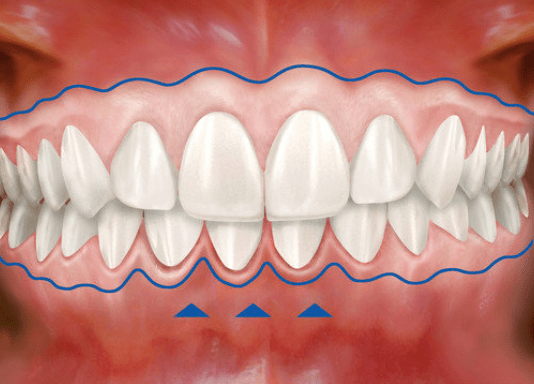
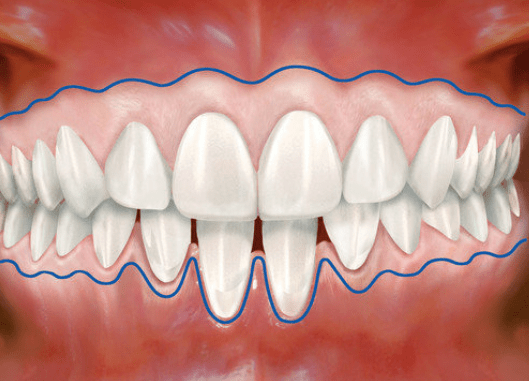
How can gum tissue be regenerated?
Geistlich Mucograft® is a clinically proven alternative to tissue transplantation. This collagen matrix supports your body’s natural gum regeneration. Your dentist will recommend the best approach for your needs.
When Your Back Teeth Are Missing
What happens when your back teeth are missing?
The roots of back teeth sit near the sinus floor — a bone layer separating sinuses from the mouth. After extraction, bone height and thickness decrease, sometimes to just 1mm. Adequate bone is essential for long-term implant stability.
How can back teeth be restored?
A sinus floor elevation can increase bone height, allowing secure implant placement. Your dentist will recommend a technique suited to your case.